 When do kids start losing teeth? Children typically start losing their baby teeth around the age of 5-6 years old. As a parent, it’s important to understand the timeline of tooth loss in children and the milestones they will go through. By knowing what to expect, you can better support your child’s dental health and ensure a smooth transition from baby teeth to permanent teeth.
When do kids start losing teeth? Children typically start losing their baby teeth around the age of 5-6 years old. As a parent, it’s important to understand the timeline of tooth loss in children and the milestones they will go through. By knowing what to expect, you can better support your child’s dental health and ensure a smooth transition from baby teeth to permanent teeth.
Key Takeaways:
- Children typically start losing their baby teeth around the age of 5-6 years old.
- Tooth loss continues until around the age of 12 years.
- The order of tooth loss follows the order of tooth eruption.
- The lower incisors are usually the first teeth to be lost.
- Regular dental care and checkups are essential for maintaining good oral health.
Order of Tooth Loss in Children
When it comes to the shedding of milk teeth, or primary teeth, children tend to follow a specific order of tooth loss. This order typically mirrors the sequence in which the teeth erupted, starting with the lower incisors. As these incisors become loose, they are the first to fall out. The upper incisors and then the lateral incisors follow suit. Molars and canines also undergo the shedding process and are eventually replaced by permanent teeth.
While the exact timing may vary for each child, there is a general pattern that most children adhere to. It is important for parents to keep track of their child’s tooth loss journey and visit a dentist regularly to ensure proper dental care.
Order of Tooth Loss in Children
| Tooth Type | Order of Loss |
|---|---|
| Lower Incisors | First |
| Upper Incisors | Second |
| Lateral Incisors | Third |
| Molars | Fourth |
| Canines | Fifth |
As seen in the table above, the lower incisors are typically the first to be lost, followed by the upper incisors, lateral incisors, molars, and canines. By understanding this order, parents can better anticipate and support their child’s dental development.
Primary Teeth Eruption Schedule
Knowing the schedule for the eruption of primary teeth, also known as baby teeth, can help parents anticipate when their child’s teeth will start to come in. Here is a breakdown of the typical sequence:
- The lower incisors – These are the front teeth on the bottom jaw and usually appear between 6 and 12 months of age.
- The lateral incisors – These are the teeth on either side of the front two teeth and usually come in a few months after the lower incisors.
- The canines – These are the pointy teeth next to the lateral incisors and usually appear between 16 and 22 months of age.
- The first molars – These are the flat teeth in the back of the mouth and typically appear between 13 and 19 months of age.
- The second molars – These are the last teeth to come in and usually appear between 25 and 33 months of age.
It’s important to note that these age ranges are approximate and can vary between children. Some children may have their teeth erupt earlier or later than the average timeline.
Monitoring your child’s primary teeth eruption schedule can help you ensure their dental development is progressing normally. If you have any concerns about your child’s teeth or if they are experiencing any discomfort during teething, it is recommended to consult with a pediatric dentist.
| Tooth Type | Average Eruption Age |
|---|---|
| Lower Incisors | 6-12 months |
| Lateral Incisors | A few months after lower incisors |
| Canines | 16-22 months |
| First Molars | 13-19 months |
| Second Molars | 25-33 months |
Remember that proper oral hygiene should start as soon as your child’s first tooth appears. Regular dental check-ups and a good dental care routine are essential for maintaining your child’s oral health as they grow.
Permanent Teeth Development
When children reach the age of 6-7 years, their primary teeth begin to fall out, making way for the development of permanent teeth. This process is a natural part of tooth development and allows for the growth of a stronger and more permanent set of teeth. The roots of the primary teeth are reabsorbed by the body, creating space for the eruption of the permanent teeth.
The development of permanent teeth typically starts with the incisors, both upper and lower. These are the front teeth that are responsible for biting and cutting food. After the incisors come in, the canines, molars, and second molars follow in a specific order. This gradual progression ensures that each tooth has enough space to grow properly and function effectively.
The timeline for permanent teeth development can vary between individuals, but most children have their permanent teeth fully developed by the age of 12. It is essential for parents to monitor their child’s dental development during this period and consult a dentist if there are any concerns or deviations from the typical timeline. Regular dental check-ups and proper oral hygiene practices can help ensure the healthy development of permanent teeth.
Timeline of Permanent Teeth Development
| Tooth Type | Typical Age of Eruption |
|---|---|
| Upper and Lower Incisors | 6-8 years |
| Canines (Cuspids) | 9-12 years |
| First Molars | 10-12 years |
| Second Molars | 11-13 years |
Please note that the ages mentioned in the table are general guidelines and may vary from child to child. It is essential to consult with a dentist to track the progress of permanent teeth development in your child and address any concerns or questions you may have.
Early Tooth Loss in Children
Early tooth loss in children can occur for various reasons and may require dental care to prevent further complications. One common cause of early tooth loss is dental caries, also known as tooth decay. Tooth decay can occur when bacteria in the mouth produce acids that erode the tooth enamel, leading to cavities. If left untreated, cavities can progress and cause the affected tooth to become loose and eventually fall out prematurely.
In addition to dental caries, other factors such as trauma or injury to the mouth can also result in early tooth loss. If a child experiences a significant impact to the mouth, it can cause the tooth to become loose or dislodged. In such cases, immediate dental attention is necessary to evaluate the extent of the injury and determine the appropriate treatment.
It is important for parents to be vigilant about their child’s oral health and seek dental care if their child experiences early tooth loss. Early intervention and treatment can help prevent further tooth loss and maintain the child’s oral health. Regular dental check-ups, proper brushing and flossing techniques, and a healthy diet can all contribute to preventing early tooth loss in children.
| Causes of Early Tooth Loss in Children | Treatment and Prevention |
|---|---|
| Dental caries (tooth decay) | Regular dental check-ups and cleanings, proper oral hygiene, healthy diet |
| Trauma or injury to the mouth | Immediate dental attention, evaluation, and treatment |
If you notice that your child is experiencing early tooth loss, it is important to consult a dentist for a thorough evaluation. The dentist can determine the underlying cause of the tooth loss and recommend appropriate treatment to prevent further complications. Remember, early intervention and proper dental care are key to maintaining your child’s oral health.
Late Tooth Loss in Children
While most children start losing their baby teeth around the age of 6, there are cases where tooth loss may occur later. Late tooth loss in children, also known as delayed loss of baby teeth, can be attributed to various factors, including delayed eruption of permanent teeth or underlying health conditions. It is important for parents to be aware of these possibilities and consult a dentist if they notice any delays or abnormalities in their child’s tooth loss process.
Table: Possible Health Conditions Delaying Tooth Loss in Children
| Health Condition | Description |
|---|---|
| Andersen-Tawil syndrome | A rare genetic disorder that can affect the development of teeth and other parts of the body. |
| Osteopetrosis autosomal recessive 2 | A genetic condition characterized by abnormal bone growth, which can impact the eruption of teeth. |
| Autosomal dominant hyper IgE syndrome | A rare immune system disorder that can affect the development of teeth and lead to delayed tooth loss. |
If a child’s delayed tooth loss affects more than one tooth or is accompanied by other symptoms, it is advisable to consult a dentist for further evaluation and guidance. The dentist will be able to assess the situation, identify any underlying causes, and recommend appropriate treatment if necessary. In most cases, late tooth loss in children is not a cause for major concern, but it is always better to seek professional advice to ensure the child’s dental health is properly managed.
How to Handle a Wiggly Tooth
When a child has a wiggly tooth, it is a sign that their baby tooth is ready to come out and make way for a permanent tooth. Handling a wiggly tooth can be an exciting and slightly nerve-wracking experience for both the child and the parents. Here are some tips on how to handle a wiggly tooth:
- Gently encourage your child to wiggle the tooth with their tongue or finger. This natural movement can help loosen the tooth further.
- If the tooth is ready to come out, you can use a piece of tissue or gauze to firmly grasp the tooth and give it a gentle twist to help it come out. Do not force the tooth out if it is not ready.
- It is important to remind your child not to pull or yank the tooth, as this can cause unnecessary pain or even damage to the surrounding gums.
If the wiggly tooth is causing significant discomfort or if you are unsure about removing it yourself, it is best to consult a dentist. They can evaluate the tooth and determine if it needs to be extracted. In some cases, a dental extraction may be necessary to ensure the healthy growth of the permanent tooth.
“Having a wiggly tooth is a normal part of growing up, and it can be an exciting milestone for children. It is important to handle a wiggly tooth with care to avoid any unnecessary pain or complications.”
Once the wiggly tooth has been successfully removed, many children have a tradition of placing it under their pillow for the tooth fairy. The tooth fairy is a beloved character in many cultures who visits children while they sleep and leaves a small gift or money in exchange for the lost tooth. This tradition adds a touch of magic and excitement to the experience of losing a tooth.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Allows space for permanent teeth to grow | Can be slightly uncomfortable or painful |
| Exciting milestone for children | May cause temporary bleeding or soreness |
| Opportunity for the tooth fairy tradition | Potential risks if tooth is forcefully removed |

Importance of Dental Care for Children
When it comes to children’s dental care, regular oral examinations play a crucial role in maintaining their oral health. These examinations not only help children become familiar with dental care but also allow dentists to identify any potential issues early on. Dental cavities are a common concern among children, with approximately 1 in 5 children aged 5-11 years having at least one decaying tooth. By adopting effective brushing techniques, practicing proper oral hygiene habits, and scheduling regular visits to the dentist, parents can help prevent dental cavities and other dental problems in their children.
One of the primary benefits of regular dental care for children is that it enables dentists to detect and address dental issues before they become more serious. During oral examinations, dentists can examine the child’s teeth and gums for signs of cavities, gum disease, and other oral health problems. They can also provide guidance on proper brushing and flossing techniques and recommend fluoride treatments to strengthen the enamel. Early detection and intervention can help prevent the need for more complex and costly dental treatments in the future.
Furthermore, dental care for children should not be limited to regular checkups alone. It is essential for parents to educate their children about the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene on a daily basis. This includes brushing teeth at least twice a day, using fluoride toothpaste, flossing regularly, and avoiding excessive consumption of sugary foods and drinks. By instilling these habits from a young age, parents can help their children develop healthy dental care routines that will benefit them throughout their lives.
Benefits of Dental Care for Children:
- Promotes early detection and prevention of dental issues
- Reduces the risk of dental cavities and gum disease
- Helps children develop lifelong oral hygiene habits
- Enhances overall oral health and well-being
In conclusion, children’s dental care, including regular oral examinations, is essential for maintaining optimal oral health. By prioritizing dental care and instilling good oral hygiene habits at a young age, parents can help their children develop healthy smiles that last a lifetime.
| Benefits of Dental Care for Children |
|---|
| Promotes early detection and prevention of dental issues |
| Reduces the risk of dental cavities and gum disease |
| Helps children develop lifelong oral hygiene habits |
| Enhances overall oral health and well-being |
Tips for Brushing and Flossing
Proper brushing and flossing techniques are essential for maintaining optimal dental hygiene in children. By establishing good oral care habits early on, parents can help prevent dental issues and promote healthy teeth and gums. Here are some tips to ensure effective brushing and flossing:
- Use a soft-bristled toothbrush: Choose a toothbrush with soft bristles that are gentle on your child’s teeth and gums. Replace the toothbrush every three to four months or sooner if the bristles become frayed.
- Brush for two minutes, twice a day: Encourage your child to brush their teeth for the recommended two minutes, twice a day. Use a timer or a fun app to make brushing more engaging and enjoyable.
- Use fluoride toothpaste: Fluoride toothpaste helps strengthen the enamel and protect against tooth decay. Use a pea-sized amount of toothpaste for children aged 3-6, and a little more for older children.
- Teach proper brushing techniques: Show your child how to brush in small, circular motions and to clean all surfaces of their teeth, including the front, back, and chewing surfaces.
- Floss daily: Introduce flossing to your child as soon as their teeth start touching each other. Use child-friendly flossers or floss picks to make it easier and more enjoyable for them.
Regular brushing and flossing remove plaque and food particles, preventing the buildup of tartar and the development of cavities. It is important to supervise your child’s brushing and flossing until they are old enough to do it effectively on their own. Encourage them to take their time and thoroughly clean their teeth and gums.
“Good dental hygiene starts with proper brushing and flossing. By teaching your child these essential habits, you are setting them up for a lifetime of healthy smiles.” – Dr. Jane Smith, Pediatric Dentist
Additionally, consider using a tartar control toothpaste to further prevent plaque buildup and tartar formation. Tartar, or hardened plaque, can only be removed by a dental professional during a cleaning. Regular dental checkups, along with consistent brushing and flossing, are crucial for maintaining your child’s dental health.
| Benefits of Brushing and Flossing | Consequences of Poor Dental Hygiene |
|---|---|
| Prevents tooth decay | Dental cavities |
| Removes plaque | Gum disease |
| Prevents bad breath | Tooth loss |
| Maintains healthy gums | Oral infections |
Dental Checkups for Children
Regular dental checkups are an essential part of maintaining children’s dental health. It is recommended to schedule dental checkups twice a year for cleaning and preventive care. These checkups help detect and prevent major dental issues, ensuring that any potential problems are identified early on. During a dental checkup, the dentist will examine the child’s teeth and gums, looking for signs of decay, cavities, or other oral health issues. X-rays may also be taken to get a comprehensive view of the child’s dental health.
Dental checkups are not just about treating existing problems; they also play a crucial role in preventive care. The dentist will provide professional cleaning, removing any plaque or tartar buildup that cannot be effectively addressed with regular brushing and flossing. Additionally, the dentist may apply dental sealants to the molars to protect them from cavities. These thin protective coatings act as a barrier, preventing food particles and bacteria from settling in the grooves of the teeth.
If a child complains of a toothache between scheduled checkups, it is important to contact the dentist for evaluation and treatment. Toothaches can be a sign of underlying dental issues that require immediate attention. Until the dental appointment, using acetaminophen can provide temporary relief from the pain. Prompt dental care can help alleviate discomfort and prevent further complications.
Table:
| Age | Recommended Dental Checkup Frequency |
|---|---|
| 0-2 years | Every 6 months |
| 2-5 years | Every 6 months |
| 6-10 years | Every 6 months |
| 10+ years | Every 6 months to 1 year |
Regular dental checkups and preventive appointments are essential for maintaining children’s dental health. These appointments help identify and address any potential issues early on, ensuring that children’s teeth and gums are healthy and strong. By establishing a routine of regular dental checkups, parents can help set their children up for a lifetime of good oral health.
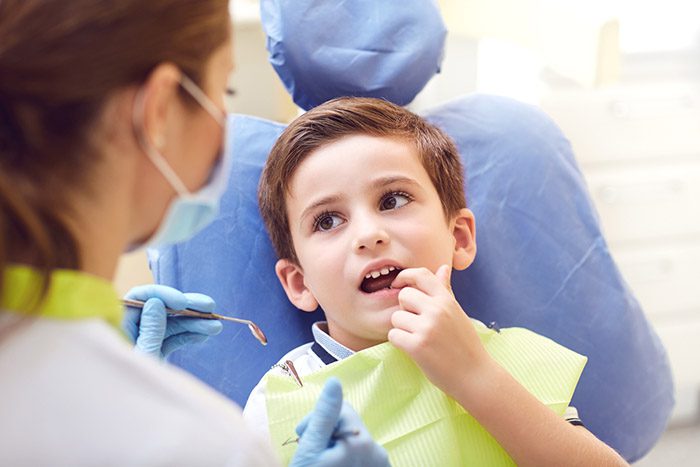
Preventing Cavities in Children
Preventing cavities is an essential aspect of maintaining children’s dental health. By implementing a few simple strategies, parents can help their children develop good oral hygiene habits and reduce the risk of cavities. Here are some key steps to prevent cavities in children:
- Brushing and Flossing: Encourage children to brush their teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste. Teach them proper brushing techniques and the importance of flossing to remove food particles and plaque.
- Healthy Diet: Limit the consumption of sugary and sticky foods, as they can contribute to tooth decay. Instead, encourage a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, which promote oral health.
- Dental Sealants: Consider the application of dental sealants to protect the molars, which are prone to cavities. Sealants create a protective barrier on the chewing surfaces of the teeth, preventing plaque and food particles from accumulating in the crevices.
- Regular Dental Checkups: Schedule regular dental checkups for your child to monitor their dental health. The dentist can identify early signs of cavities and provide preventive treatments such as fluoride application to strengthen the teeth.
By following these preventive measures, parents can help their children maintain healthy and cavity-free teeth. It is important to lead by example and make dental care a priority in the family’s daily routine. Remember, prevention is the key to long-term oral health!
| Preventive Measures | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Regular brushing and flossing | Removes plaque and food particles, reducing the risk of cavities. |
| Healthy diet | Minimizes exposure to sugary foods, which can cause tooth decay. |
| Dental sealants | Creates a protective barrier on molars, preventing cavities. |
| Regular dental checkups | Allows for early detection and treatment of cavities. |
By implementing these preventive measures, parents can significantly reduce the risk of cavities in their children. Teaching good oral hygiene habits and providing regular dental care sets the foundation for a lifetime of healthy smiles.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the process of losing baby teeth in children is a natural and important milestone in their dental development. It typically begins around the age of 6–7 and continues until around 12 years old. The order of tooth loss generally follows the order of tooth eruption, with the lower incisors being the first to be lost. It’s important to note that early or late tooth loss in children can sometimes be indicative of underlying health conditions or dental problems.
To ensure optimal dental health, regular dental care is essential. This includes regular oral examinations, proper brushing and flossing techniques, and regular dental checkups. Preventive measures such as dental sealants and maintaining a healthy diet can significantly reduce the risk of cavities and other dental issues.
Overall, by following these dental care practices, parents can help their children maintain good oral hygiene and set them up for a lifetime of healthy teeth and gums. Remember, a healthy smile contributes not only to physical well-being but also to self-confidence and overall quality of life.
FAQ
When do kids start losing their baby teeth?
Children usually start losing their baby teeth around the age of 5-6 years.
What is the order of tooth loss in children?
The order of tooth loss usually follows the order of tooth eruption, with the lower incisors being the first to be lost.
What is the schedule for primary teeth eruption?
Primary teeth, also known as baby teeth, typically follow a schedule, with the lower incisors appearing first, usually around 6–12 months of age.
When do permanent teeth start developing?
Permanent teeth development usually begins around the age of 6–7 years when children start losing their primary teeth.
What can cause early tooth loss in children?
Early tooth loss in children can be caused by factors such as premature eruption of primary teeth or dental caries (tooth decay).
Why do some children experience late tooth loss?
Late tooth loss in children may be caused by factors such as delayed eruption of permanent teeth or underlying health conditions.
How should I handle a wiggly tooth in my child?
It is best to let the wiggly tooth come out naturally, but if necessary, it can be gently twisted to remove it.
Why is dental care important for children?
Dental care is essential for children to maintain good oral health and prevent dental issues.
What are some tips for brushing and flossing in children?
Children may need assistance with brushing their teeth until they are between 7 and 10 years old. Regular flossing and use of tartar-control toothpaste are also important.
How often should children have dental checkups?
It is recommended to schedule dental checkups twice a year for cleaning and preventive care.
How can cavities be prevented in children?
Cavities can be prevented in children through regular brushing, flossing, limiting sugary snacks, and applying dental sealants.




